I. Introduction
In the realm of healthcare, few scenarios evoke as much urgency and concern as pediatric emergencies. The delicate nature of treating children in critical conditions requires specialized knowledge, swift action, and a steady hand. Amidst this backdrop, the American Heart Association Pediatric Advanced Life Support (AHA PALS) program emerges as a beacon of hope, providing healthcare providers with the tools and expertise needed to navigate pediatric emergencies effectively.
A. Brief Overview of Pediatric Emergency Care
Pediatric emergency care encompasses the specialized medical attention provided to infants, children, and adolescents in acute and critical situations. These emergencies can range from respiratory distress and cardiac arrest to traumatic injuries and severe infections. Due to anatomical and physiological differences between children and adults, pediatric patients require tailored approaches and interventions to optimize outcomes.
B. Introduction to AHA PALS
At the forefront of pediatric emergency care stands the American Heart Association Pediatric Advanced Life Support (AHA PALS) program. AHA PALS is a comprehensive training and certification program designed to equip healthcare providers with the knowledge, skills, and confidence needed to manage pediatric emergencies effectively. Rooted in evidence-based guidelines and best practices, AHA PALS empowers healthcare professionals to deliver timely and proficient care to pediatric patients in critical conditions.
II. Understanding AHA PALS
A. Definition and Significance of AHA PALS
The American Heart Association Pediatric Advanced Life Support (AHA PALS) program is a specialized training curriculum developed to equip healthcare providers with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively manage pediatric emergencies. Recognizing the unique physiological and anatomical differences between pediatric and adult patients, AHA PALS focuses on evidence-based approaches tailored specifically to the needs of children in critical conditions.
The significance of AHA PALS lies in its ability to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application in pediatric emergency care. By standardizing protocols and emphasizing hands-on training, AHA PALS ensures that healthcare providers are prepared to deliver timely and proficient care in high-stress situations, ultimately improving outcomes for pediatric patients.
B. Evolution and Development of AHA PALS Guidelines
Since its inception, the AHA PALS program has evolved in response to advancements in medical science, changes in clinical practice, and emerging trends in pediatric emergency care. Guided by a robust framework of research and consensus-based recommendations, the development of AHA PALS guidelines is a dynamic process aimed at continually refining and enhancing the standard of care for pediatric patients.
Through ongoing collaboration with pediatric experts, healthcare professionals, and stakeholders in the field, the AHA PALS guidelines undergo regular updates to reflect the latest evidence and best practices. This iterative approach ensures that AHA PALS remains at the forefront of pediatric emergency medicine, equipping healthcare providers with the most current knowledge and strategies to address evolving clinical challenges.
C. Key Components of AHA PALS Certification
Achieving AHA PALS certification entails the completion of a structured curriculum that covers essential concepts, skills, and interventions relevant to pediatric advanced life support. The certification process typically includes the following key components:
- Training Requirements: Healthcare providers seeking AHA PALS certification must undergo comprehensive training, which may be delivered through traditional classroom-based courses, online modules, or blended learning formats. These courses are facilitated by certified instructors who guide participants through didactic lectures, interactive discussions, and hands-on skills stations.
- Skills Assessment: A critical aspect of AHA PALS certification involves the demonstration of proficiency in key skills and interventions related to pediatric advanced life support. Participants are evaluated through simulated scenarios that replicate real-life emergencies, allowing them to apply their knowledge and expertise in a controlled environment under the guidance of instructors.
- Renewal Process: AHA PALS certification is typically valid for a specified period, after which healthcare providers are required to undergo renewal to maintain their credentials. Renewal may involve completing refresher courses, participating in continuing education activities, and passing competency assessments to ensure ongoing competence and readiness to respond to pediatric emergencies.
III. Importance of AHA PALS in Pediatric Emergency Care
A. Enhancing Patient Outcomes
The primary objective of pediatric emergency care is to optimize patient outcomes, and AHA PALS plays a pivotal role in achieving this goal. By equipping healthcare providers with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to effectively manage pediatric emergencies, AHA PALS facilitates timely interventions that can significantly impact patient survival and recovery.
- Timely Intervention in Critical Situations: Pediatric emergencies often require rapid and decisive action to stabilize the patient and prevent further deterioration. AHA PALS emphasizes the importance of early recognition and intervention, guiding healthcare providers through systematic approaches to assessment, resuscitation, and treatment. By instilling a sense of urgency and readiness to act, AHA PALS helps minimize delays in care delivery, thereby improving outcomes for pediatric patients in critical conditions.
- Application of Evidence-Based Protocols: AHA PALS is founded on evidence-based guidelines and protocols that have been rigorously evaluated and validated through clinical research. These guidelines serve as a roadmap for healthcare providers, offering standardized approaches to the assessment and management of common pediatric emergencies such as cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, and shock. By adhering to established protocols, healthcare providers can ensure consistency and quality of care, leading to better outcomes for pediatric patients.
B. Strengthening Healthcare Provider Skills
In addition to benefiting patients, AHA PALS also plays a crucial role in enhancing the skills and competence of healthcare providers who care for pediatric patients. Through comprehensive training and hands-on practice, AHA PALS equips healthcare professionals with the expertise needed to deliver high-quality care in complex and challenging situations.
- Advanced Resuscitation Techniques: Pediatric cardiac arrest poses unique challenges that require specialized knowledge and skills to manage effectively. AHA PALS provides healthcare providers with advanced resuscitation techniques tailored specifically to pediatric patients, including high-quality CPR, defibrillation, and medication administration. By mastering these techniques, healthcare providers can maximize the chances of successful resuscitation and improve outcomes for pediatric patients in cardiac arrest.
- Team Dynamics and Communication: Effective teamwork and communication are essential components of pediatric emergency care, where multiple healthcare providers must collaborate seamlessly to deliver coordinated care. AHA PALS emphasizes the importance of teamwork and communication skills through simulated scenarios that simulate real-life emergencies. By fostering collaboration, leadership, and effective communication within healthcare teams, AHA PALS enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of pediatric emergency response.
C. Addressing Specific Pediatric Emergencies
Pediatric patients present with a diverse range of medical conditions and emergencies, each requiring a tailored approach to assessment and management. AHA PALS equips healthcare providers with the knowledge and skills needed to address a wide spectrum of pediatric emergencies, including:
- Cardiac Arrest: AHA PALS provides healthcare providers with the tools and strategies needed to effectively manage pediatric cardiac arrest, including the recognition of rhythms, initiation of CPR, and use of advanced life support interventions such as defibrillation and medication administration.
- Respiratory Distress: Respiratory emergencies are common in pediatric patients and require prompt intervention to ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation. AHA PALS emphasizes the assessment and management of respiratory distress, including airway management, oxygen therapy, and ventilation support techniques.
- Shock: Pediatric shock is a life-threatening condition characterized by inadequate tissue perfusion and oxygen delivery. AHA PALS teaches healthcare providers to recognize the signs and symptoms of shock and implement appropriate interventions to restore hemodynamic stability and improve perfusion.
- Arrhythmias: Pediatric arrhythmias can have serious consequences and require prompt recognition and management to prevent adverse outcomes. AHA PALS educates healthcare providers on the identification and treatment of common pediatric arrhythmias, including bradycardia, tachycardia, and pulseless electrical activity.
By addressing these specific pediatric emergencies, AHA PALS empowers healthcare providers to deliver timely and effective care, ultimately improving outcomes for pediatric patients in critical conditions.
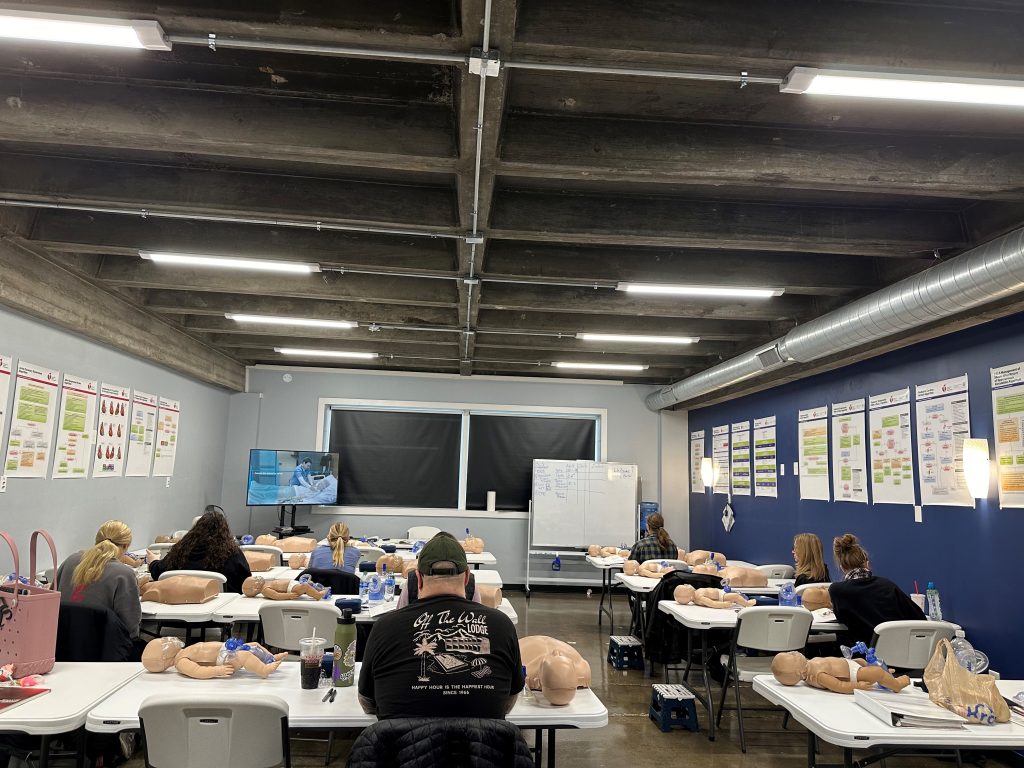

IV. AHA PALS Training and Certification Process
A. Overview of AHA PALS Courses
The journey toward AHA PALS certification begins with participation in a structured training course that covers the essential concepts, skills, and interventions necessary for pediatric advanced life support. These courses are designed to accommodate the diverse learning needs of healthcare providers and are available in various formats, including:
- Classroom-Based Training: Traditional classroom-based AHA PALS courses offer participants the opportunity to engage in face-to-face instruction led by certified instructors. These courses typically feature interactive lectures, hands-on skills stations, and simulated scenarios that replicate real-life pediatric emergencies. Classroom-based training allows for direct interaction with instructors and peers, fostering collaborative learning and skill development.
- Online Courses: AHA PALS courses are also available in online formats, providing flexibility and convenience for healthcare providers with busy schedules or limited access to in-person training. Online courses feature interactive modules, multimedia presentations, and self-paced learning activities that allow participants to study at their own pace and convenience. Online courses may be supplemented with in-person skills sessions or virtual simulations to ensure competency in hands-on skills.
- Blended Learning Options: Blended learning combines online and in-person components to offer a flexible and comprehensive training experience. Participants begin by completing online modules at their own pace, followed by hands-on skills sessions and simulated scenarios conducted in a classroom setting. Blended learning allows healthcare providers to benefit from the convenience of online learning while still receiving valuable hands-on instruction and feedback from certified instructors.
B. Examination and Skills Assessment
Upon completion of the AHA PALS course, healthcare providers must demonstrate proficiency in key concepts and skills through a combination of written examinations and skills assessments. The examination component typically consists of a standardized test covering the theoretical aspects of pediatric advanced life support, including core concepts, algorithms, and treatment guidelines.
In addition to the written examination, healthcare providers are required to undergo skills assessments to evaluate their ability to perform essential interventions and procedures related to pediatric advanced life support. Skills assessments may include simulated scenarios that replicate common pediatric emergencies, allowing participants to demonstrate their ability to assess patients, initiate appropriate interventions, and communicate effectively within a multidisciplinary team.
C. Certification and Renewal Requirements
Successful completion of the AHA PALS course and assessment components leads to certification as a Pediatric Advanced Life Support Provider, valid for a specified period typically ranging from one to two years. To maintain certification, healthcare providers must fulfill renewal requirements, which may include:
- Renewal Courses: AHA PALS certification renewal courses are designed to update healthcare providers on the latest guidelines, protocols, and evidence-based practices in pediatric advanced life support. Renewal courses may be offered in traditional classroom-based formats, online modules, or blended learning options to accommodate diverse learning preferences.
- Continuing Education: Participation in continuing education activities related to pediatric emergency care is often a requirement for AHA PALS certification renewal. Healthcare providers may earn continuing education credits by attending conferences, workshops, seminars, or online courses focused on pediatric advanced life support and related topics.
- Competency Assessments: AHA PALS certification renewal may also involve competency assessments to ensure that healthcare providers maintain proficiency in essential skills and interventions. Competency assessments may include skills demonstrations, simulated scenarios, or written examinations designed to evaluate knowledge retention and clinical competence.
By adhering to certification and renewal requirements, healthcare providers demonstrate their ongoing commitment to excellence in pediatric emergency care and ensure that they remain equipped to respond effectively to pediatric emergencies in clinical practice.
V. Integrating AHA PALS into Clinical Practice
A. Implementing AHA PALS Guidelines in Healthcare Settings
The successful integration of AHA PALS guidelines into clinical practice is essential for ensuring consistent and effective management of pediatric emergencies across healthcare settings. Healthcare institutions can promote the adoption of AHA PALS principles through various strategies, including:
- Standardized Protocols: Establishing standardized protocols and algorithms based on AHA PALS guidelines ensures consistency and uniformity in the assessment and management of pediatric emergencies. These protocols should be readily accessible to healthcare providers and integrated into clinical workflows to facilitate prompt and appropriate interventions.
- Interdisciplinary Training: Collaborative training sessions involving healthcare providers from various disciplines, including physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, and emergency medical personnel, to help foster a multidisciplinary approach to pediatric advanced life support. By training together as a cohesive team, healthcare providers can enhance communication, coordination, and teamwork in pediatric emergency situations.
- Simulation-Based Education: Simulation-based education is a valuable tool for reinforcing AHA PALS principles and enhancing clinical competence in pediatric emergency care. Healthcare institutions can utilize high-fidelity simulation scenarios to simulate realistic pediatric emergencies and provide hands-on training to healthcare providers. These simulations allow participants to practice critical skills, refine decision-making abilities, and enhance confidence in managing pediatric emergencies.
B. Role of Simulation-Based Training in AHA PALS
Simulation-based training plays a critical role in AHA PALS education by providing healthcare providers with opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in realistic clinical scenarios. Through simulation, healthcare providers can develop and refine essential skills in pediatric advanced life support, including:
- Rapid Assessment: Simulated scenarios allow healthcare providers to practice rapid and systematic patient assessment, including the identification of critical conditions, recognition of deteriorating clinical status, and prioritization of interventions based on patient needs.
- Effective Communication: Communication is essential in pediatric emergency situations, where clear and concise communication among team members is crucial for ensuring coordinated care. Simulation-based training enables healthcare providers to practice effective communication strategies, including closed-loop communication, team briefings, and debriefings.
- Crisis Resource Management: Crisis resource management (CRM) principles emphasize the importance of leadership, teamwork, situational awareness, and decision-making in high-stress environments. Simulation-based training provides healthcare providers with opportunities to develop and enhance CRM skills, allowing them to effectively manage pediatric emergencies as part of a cohesive team.
- Technical Skills Proficiency: Simulation allows healthcare providers to practice technical skills, such as airway management, vascular access, medication administration, and defibrillation, in a safe and controlled environment. By repeatedly performing these skills under realistic conditions, healthcare providers can build confidence and proficiency in pediatric advanced life support interventions.
C. Collaboration and Coordination Within Healthcare Teams
Effective collaboration and coordination among healthcare teams are essential for optimizing patient outcomes in pediatric emergencies. AHA PALS emphasizes the importance of teamwork and communication skills, which are essential components of effective pediatric advanced life support. Healthcare providers must work together seamlessly to assess patients, implement interventions, and monitor responses to treatment.
- Team Dynamics: AHA PALS training emphasizes the importance of clear roles and responsibilities within healthcare teams, ensuring that each team member understands their role in pediatric emergencies. By establishing clear leadership structures, defining roles and responsibilities, and promoting mutual respect and trust among team members, healthcare teams can function cohesively and efficiently in pediatric emergencies.
- Communication Strategies: Effective communication is critical for ensuring that vital information is conveyed accurately and efficiently among healthcare team members during pediatric emergencies. AHA PALS emphasizes communication strategies such as closed-loop communication, briefings, and debriefings, which help facilitate clear and concise communication among team members.
- Debriefing and Reflection: Debriefing sessions following simulated scenarios or real-life pediatric emergencies provide opportunities for healthcare providers to reflect on their performance, identify areas for improvement, and discuss lessons learned. AHA PALS encourages debriefing as a valuable tool for promoting continuous learning, enhancing teamwork, and fostering a culture of safety and excellence in pediatric emergency care.
By embracing the principles of collaboration and coordination within healthcare teams, healthcare institutions can enhance the delivery of pediatric advanced life support and improve outcomes for pediatric patients in critical conditions.
VI. Challenges and Future Directions
A. Addressing Barriers to AHA PALS Implementation
While AHA PALS is a cornerstone in pediatric emergency care, its successful implementation may face challenges within healthcare systems. Common barriers include
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources, including time and budget constraints, may hinder healthcare providers’ access to comprehensive AHA PALS training. Addressing these constraints requires a commitment to prioritizing pediatric advanced life support education and allocating resources to support ongoing training and certification efforts.
- Educational Awareness: Ensuring that healthcare providers are aware of the benefits and importance of AHA PALS is crucial. Educational initiatives and awareness campaigns can help promote the value of AHA PALS certification and encourage healthcare providers to pursue training.
- Integration into Clinical Practice: Incorporating AHA PALS principles into routine clinical practice may face resistance or challenges related to established workflows and practices. To overcome this, healthcare institutions should actively promote and support the integration of AHA PALS guidelines into their standard operating procedures.
B. Emerging Trends and Advancements in Pediatric Emergency Care
Pediatric emergency care is a dynamic field, and ongoing advancements contribute to the continuous improvement of patient outcomes. Key trends and developments include:
- Technological Innovations: The integration of advanced technologies, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, into AHA PALS training, may offer immersive and realistic simulations, enhancing the educational experience for healthcare providers.
- Telemedicine in Pediatric Emergencies: Telemedicine has the potential to play a significant role in pediatric emergency care, allowing remote consultation and support for healthcare providers in underserved or remote areas. Future developments may focus on incorporating telemedicine into AHA PALS training and emergency response strategies.
- Pediatric Simulation Research: Ongoing research in pediatric simulation aims to refine and expand the use of simulation-based training in AHA PALS. This research may lead to the development of more realistic and scenario-specific simulations, further enhancing the effectiveness of pediatric advanced life support education.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the American Heart Association Pediatric Advanced Life Support (AHA PALS) program stands as a crucial pillar in pediatric emergency care. By providing healthcare providers with specialized training, evidence-based guidelines, and hands-on skills, AHA PALS empowers professionals to deliver optimal care to pediatric patients in critical conditions.
From the early stages of recognizing the importance of pediatric emergency care to understanding the evolution of AHA PALS guidelines and the practical aspects of certification, this exploration has highlighted the vital role AHA PALS plays in enhancing patient outcomes and healthcare provider skills. By integrating AHA PALS principles into clinical practice, healthcare institutions can foster a culture of excellence, teamwork, and continuous improvement in pediatric emergency care.
As we navigate the challenges and embrace emerging trends in pediatric emergency care, the commitment to AHA PALS remains a cornerstone for ensuring that healthcare providers are well-prepared to respond effectively to the unique needs of pediatric patients. By addressing barriers, staying abreast of advancements, and fostering a culture of ongoing education and collaboration, the healthcare community can continue to elevate the standard of pediatric emergency care and make a lasting impact on the well-being of children in critical situations.




