In the critical moments following cardiac arrest, every second counts. While high-quality CPR remains the foundation of resuscitation efforts, the integration of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) has revolutionized emergency response protocols. This guide explores how effectively incorporating AEDs into your CPR and Basic Life Support (BLS) practices can significantly improve survival outcomes and why proper training is essential for all healthcare providers and laypersons alike.
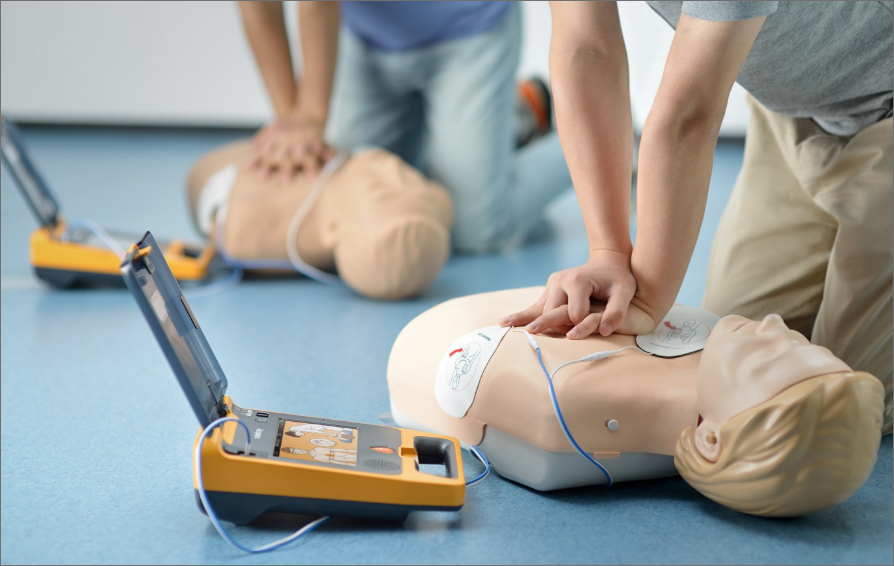
The Critical Role of Integrating AEDs in Emergency Response
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) affects more than 356,000 individuals outside hospital settings annually in the United States alone. Without prompt intervention, survival rates decrease by 7-10% for every minute that passes without defibrillation. While CPR helps maintain blood circulation and oxygen delivery to vital organs, it alone cannot restore a normal heart rhythm in cases of ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia—the most common arrhythmias in cardiac arrest.
AEDs address this critical gap by analyzing the heart’s electrical activity and delivering a controlled shock when necessary to reset the heart’s rhythm. Research has consistently demonstrated that early defibrillation, when combined with effective CPR, can increase survival rates from less than 10% to over 50% in certain settings.
Understanding the AED Advantage
Integrating AEDs into emergency response protocols offers several distinct advantages:
- Simplified Lifesaving Technology: Modern AEDs require minimal training to operate effectively, using voice prompts and visual cues to guide users through the resuscitation process.
- Rapid Assessment Capability: AEDs quickly analyze heart rhythms and determine whether defibrillation is necessary, eliminating guesswork during critical moments.
- Customized Energy Delivery: Advanced AEDs adjust shock energy based on the patient’s impedance, ensuring optimal defibrillation while minimizing potential tissue damage.
- Data Recording and Transfer: Many AEDs now record critical event data, including heart rhythms and response times, which can be transferred to emergency medical services and hospitals for continued care.
Integrating AEDs with CPR: The Chain of Survival
The American Heart Association’s Chain of Survival emphasizes five critical links in addressing cardiac emergencies:
- Recognition of cardiac arrest and activation of emergency response
- Early CPR with emphasis on chest compressions
- Rapid defibrillation
- Advanced resuscitation by EMS and other healthcare providers
- Post-cardiac arrest care
Effectively integrating AEDs addresses the crucial third link while supporting the overall chain. Current guidelines recommend minimizing interruptions in chest compressions, even when using an AED. This integrated approach maximizes blood circulation while preparing for and delivering potentially lifesaving defibrillation.
Practical Tips for Integrating AEDs into Your CPR Response
For healthcare providers and trained responders, these strategies can help seamlessly incorporate AEDs into resuscitation efforts:
- Minimize Compression Interruptions: Designate specific team members to manage the AED while others maintain continuous compressions until the device is ready to analyze.
- Coordinate Rhythm Checks: Synchronize CPR pauses with AED rhythm analysis to minimize hands-off time.
- Clear Communication: Establish clear verbal commands when preparing to analyze rhythms or deliver shocks to ensure safety and coordination.
- Position for Efficiency: Place the AED on the same side as the person operating it, opposite the chest compressor, to minimize crowding and optimize workflow.
- Anticipate Next Steps: While performing CPR, mentally prepare for AED application steps to reduce delays.
Integrating AEDs into Different Care Settings
The approach to AED integration varies based on the care environment and available resources.
Hospital Settings
In hospitals, code teams typically include designated AED/defibrillator operators. Integration challenges often involve:
- Transitioning from manual CPR to mechanical devices while maintaining defibrillator readiness
- Coordinating multiple interventions, including medication administration and advanced airway management
- Ensuring compatible monitoring systems between transport and critical care areas
Best practices include regular team simulations, clearly defined roles, and standardized equipment placement throughout the facility.
Outpatient and Clinic Settings
For outpatient facilities, consider these integration strategies:
- Strategic AED placement with visual indicators showing device locations
- Regular staff drills using actual facility layout and equipment
- Designated emergency response teams with defined AED responsibilities
- Integration with local EMS systems for seamless handoffs
Community and Public Settings
Public access defibrillation programs require:
- Visible placement with standardized signage
- Regular maintenance checks and battery monitoring
- Community awareness campaigns about AED locations
- Integration with citizen responder mobile apps and 911 systems
- Simplified instructions for layperson use
Overcoming Barriers to Effective AED Integration
Despite their proven benefits, several obstacles can hinder effective AED integration:
Psychological Barriers
Many potential responders fear making mistakes or causing harm. Addressing these concerns requires:
- Emphasizing AED safety features that prevent inappropriate shocks
- Regular hands-on practice to build confidence
- Reinforcing the significant survival benefit of early defibrillation
- Highlighting the user-friendly design of modern devices
Logistical Challenges
Practical implementation issues include:
- Maintenance Requirements: Establishing systematic checking of batteries, pads, and device functionality
- Placement Decisions: Balancing accessibility with protection from theft or damage
- Registration Compliance: Ensuring devices meet local registry requirements and EMS integration
- Funding Limitations: Exploring grants, donations, and shared-cost models for acquisition
Training Consistency
Maintaining skill proficiency requires:
- Scheduled refresher training aligned with certification renewals
- Surprise drills to test real-world readiness
- Scenario-based training that integrates CPR and AED use
- Team-based approaches that mirror actual emergency response workflows
Integrating AEDs into Your BLS Training and Certification
For healthcare providers, BLS certification now heavily emphasizes integrated AED use. When selecting training programs, prioritize courses that offer:
Hands-On Skills Development
Quality BLS programs should provide:
- Multiple practice opportunities with different AED models
- Scenarios requiring coordinated CPR and defibrillation
- Team-based resuscitation simulations
- Performance feedback from experienced instructors
Real-World Applications
Effective training bridges classroom learning and practical application by:
- Discussing AED locations in participants’ specific work environments
- Addressing unique considerations for different patient populations
- Practicing with the exact AED models used in their facilities
- Simulating common complications and troubleshooting scenarios
Continuous Improvement
The science of resuscitation continues to evolve. Ongoing development includes:
- Updates on the latest AHA guidelines and evidence-based practices
- Discussion of emerging technologies in defibrillation
- Review of recent case studies demonstrating successful integrations
- Resources for continuing education between certification periods
The Future of AED Integration in Resuscitation
As technology advances, we can expect further innovations in AED design and integration:
- Smaller, More Portable Devices: Increasingly compact units enabling more widespread deployment
- Enhanced Connectivity: Real-time transmission of cardiac data to incoming emergency services
- Advanced Feedback Systems: Devices providing CPR quality feedback alongside defibrillation capability
- Public Integration: Smart city initiatives incorporating AED mapping and dispatcher guidance
- AI-Enhanced Analysis: More sophisticated rhythm analysis reducing false positives and negatives
Key Takeaways for Optimizing AED Integration
To maximize the effectiveness of AEDs in resuscitation efforts:
- Train Frequently: Maintain skills through regular practice beyond minimum certification requirements.
- Plan Strategically: Develop facility-specific protocols for AED deployment and use.
- Minimize Delays: Implement systems ensuring rapid access to devices when needed.
- Practice as Teams: Rehearse coordinated responses involving multiple responders.
- Stay Current: Regularly update knowledge based on evolving guidelines and technology.
Call to Action
Don’t wait until an emergency to develop your AED integration skills. CPR Tampa, an American Heart Association training site in Tampa, offers comprehensive, hands-on training that will prepare you to respond confidently in cardiac emergencies.
Our stress-free, hands-on CPR certification Tampa courses provide the skills and confidence needed to effectively integrate AED use with high-quality CPR. Healthcare professionals seeking BLS certification in Tampa can benefit from our specialized programs designed to meet AHA requirements while emphasizing real-world application.
Whether you need initial certification or renewal in BLS for Healthcare Providers, ACLS, PALS, or CPR and First Aid courses, our experienced instructors ensure you develop the competence and confidence to save lives. Contact Best CPR in Tampa today to schedule your training and become part of the critical chain of survival in our community.
By properly integrating AEDs into your CPR and BLS practices, you’re not just following protocols—you’re optimizing every aspect of your emergency response to give cardiac arrest victims their best chance at survival.




