I. CPR Techniques in BLS
Basic Life Support (BLS) is a crucial set of medical procedures and skills designed to support life until more advanced medical treatment can be administered. At the heart of BLS training lies Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR), a lifesaving technique used in emergencies such as cardiac arrest or near-drowning incidents.
CPR is a critical component of BLS training because it can mean the difference between life and death for someone experiencing a cardiac emergency. When performed correctly, CPR helps maintain blood flow to vital organs, particularly the brain, which can prevent or minimize long-term damage until professional medical help arrives.
In BLS training, participants learn not only the fundamental techniques of CPR but also how to recognize life-threatening situations, activate the emergency response system, and use an Automated External Defibrillator (AED). These skills empower individuals to act quickly and confidently in crises, potentially saving lives in their communities, workplaces, or even at home.
As we delve into the essential CPR techniques taught in BLS training, it’s important to note that while this article provides an overview, it is not a substitute for proper training. Hands-on practice under professional guidance is crucial for developing the skills and confidence needed to perform CPR effectively in real-life situations.
II. Chest Compressions
The cornerstone of effective CPR is high-quality chest compressions. BLS training emphasizes the following key aspects:
- Proper hand placement To perform chest compressions correctly, rescuers are taught to place the heel of one hand in the center of the victim’s chest, specifically on the lower half of the breastbone (sternum). The other hand is then placed on top, interlocking the fingers to ensure consistent pressure distribution.
B. Compression depth and rate
BLS training emphasizes the importance of proper compression depth and rate for effective CPR. For adults, rescuers are taught to compress the chest to a depth of at least 2 inches (5 cm) but no more than 2.4 inches (6 cm). This depth ensures adequate blood flow to vital organs.
The recommended compression rate is 100 to 120 compressions per minute. This pace is often described as “pushing to the beat of the disco song ‘Stayin’ Alive'” to help rescuers maintain the correct rhythm.
C. Allowing full chest recoil
After each compression, it’s crucial to allow the chest to fully recoil or return to its normal position. This allows the heart to refill with blood between compressions, improving the overall effectiveness of CPR. Rescuers are taught not to lean on the chest between compressions, as this can prevent full recoil.
III. Rescue Breaths
While chest compressions are the primary focus of modern CPR, rescue breaths remain an important component, especially for healthcare providers and those comfortable with the technique. BLS training covers:
A. Opening the airway
Before giving rescue breaths, it’s essential to ensure the airway is open. This is typically done using the head-tilt, chin-lift maneuver. The rescuer tilts the victim’s head back slightly and lifts the chin to open the airway.
B. Mouth-to-mouth technique
For mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, rescuers are taught to:
- Pinch the victim’s nose closed
- Create a seal over the victim’s mouth with their own
- Give two rescue breaths, each lasting about 1 second
- Watch for the chest to rise with each breath
C. Bag-valve-mask ventilation
In healthcare settings or when available, a bag-valve-mask (BVM) device is often used instead of mouth-to-mouth breathing. BLS training covers the proper technique for using a BVM, including:
- Selecting the appropriate mask size
- Creating a proper seal on the victim’s face
- Squeezing the bag to deliver breaths
- Observing chest rise to ensure effective ventilation
IV. CPR Sequence
BLS training emphasizes a specific sequence of actions for performing CPR:
A. Check scene safety and responsiveness
Before approaching a victim, rescuers are taught to ensure the scene is safe. Once safety is confirmed, they check for responsiveness by tapping the victim’s shoulder and shouting, “Are you okay?”
B. Activate emergency response system
If the victim is unresponsive, the next step is to activate the emergency response system. In most areas, this means calling 911 or the local emergency number. If others are present, one person should begin CPR while another calls for help.
C. 30:2 compression-to-ventilation ratio
For adult CPR, rescuers are taught to perform 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths. This cycle is repeated until professional help arrives, an AED is ready to use, or the victim shows signs of life.
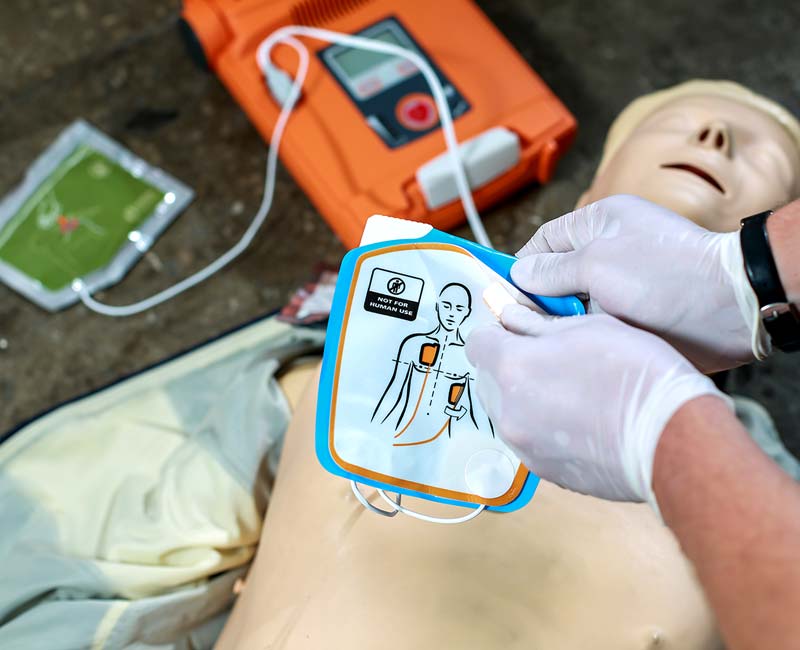
V. AED (Automated External Defibrillator) Use
AEDs are critical devices in improving survival rates for sudden cardiac arrest. BLS training covers the following aspects of AED use:
A. When and how to use an AED
Rescuers are taught to use an AED as soon as it becomes available. The steps for AED use include:
- Turn on the AED and follow its audio/visual prompts
- Expose the victim’s chest
- Dry the chest if necessary
- Apply the AED pads
B. Pad placement
Proper pad placement is crucial for effective defibrillation. Typically, one pad is placed on the upper right chest below the collarbone, and the other on the lower left side of the chest. AEDs often have diagrams on the pads to guide correct placement.
C. Following AED prompts
Modern AEDs provide clear voice and/or visual instructions. Rescuers are taught to:
- Clear the area around the victim when the AED is analyzing the heart rhythm
- Ensure no one is touching the victim when the shock is delivered
- Resume CPR immediately after a shock is delivered or if no shock is advised
VI. Special Considerations
BLS training also covers modifications for specific situations:
A. Infant and child CPR modifications
CPR techniques are slightly different for infants and children:
- Use two fingers for chest compressions on infants
- Compress to a depth of about 1.5 inches for infants and 2 inches for children
- Use a gentler breath for rescue breathing
B. Two-rescuer CPR techniques
When two trained rescuers are available, they can work together more efficiently:
- One rescuer performs compressions while the other gives breaths
- Switch roles every 2 minutes to prevent fatigue
- Use a 15:2 compression-to-ventilation ratio for infant and child CPR
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering essential CPR techniques through BLS training can mean the difference between life and death in emergencies. These vital skills empower individuals to act swiftly and confidently when every second counts. By learning proper chest compressions, rescue breaths, and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs), you can become a crucial link in the chain of survival.
Don’t wait for an emergency to strike – take action now to prepare yourself. Enroll in CPR Certification and BLS certification Indianapolis courses to gain the knowledge and skills needed to save lives. CPR Indianapolis, an American Heart Association training site, offers comprehensive, stress-free, and hands-on classes for both initial certifications and renewals.
Whether you’re a healthcare professional seeking BLS for Healthcare Providers, ACLS, or PALS certification, or an individual interested in CPR and First Aid courses, CPR Indianapolis has you covered. Their expert instructors ensure you receive the best CPR training in Indianapolis, equipping you with confidence and competence to handle critical situations.
Invest in yourself and your community by obtaining your CPR certification in Indianapolis today. Remember, the life you save could be that of a loved one. Visit CPR Indianapolis to explore their course offerings and take the first step towards becoming a certified lifesaver.