When faced with a medical emergency, every second counts. The DRSABCD protocol provides a systematic approach that can help anyone respond effectively to emergencies. This step-by-step guide has saved countless lives worldwide and serves as the foundation for modern first aid training.
Understanding the DRSABCD Framework
The DRSABCD acronym represents seven critical steps in emergency response: Danger, Response, Send for help, Airway, Breathing, CPR, and Defibrillation. This systematic approach ensures that responders address emergencies in the correct order, maximizing the chances of a positive outcome.
Medical professionals and trained responders rely on this protocol because it provides structure during high-stress situations. Moreover, the DRSABCD system helps prevent common mistakes that can occur when people panic during emergencies.
Step 1: Danger Assessment in DRSABCD
The first step in the DRSABCD protocol focuses on identifying and managing potential hazards. Before approaching any emergency scene, responders must carefully evaluate the environment for dangers that could harm both the victim and themselves.
Common dangers include electrical hazards, fire, toxic fumes, unstable structures, or violent situations. Additionally, traffic accidents present ongoing risks from moving vehicles. The key principle remains simple: never put yourself at risk, as this could create additional victims requiring rescue.
If dangers are present, responders should either eliminate them safely or wait for professional help. Furthermore, establishing a safe perimeter protects both the victim and potential responders from further harm.
Step 2: Response – Checking Consciousness in DRSABCD
After ensuring safety, the DRSABCD protocol requires checking the victim’s level of consciousness. This assessment helps determine the appropriate course of action and the urgency of the situation.
The recommended approach involves speaking loudly and clearly to the person, asking simple questions like “Are you okay?” or “Can you hear me?” If there’s no verbal response, gentle physical stimulation may be necessary. However, avoid shaking someone who might have spinal injuries.
Conscious victims can often provide valuable information about their condition. Meanwhile, unconscious victims require immediate progression through the remaining DRSABCD steps.
Step 3: Send for Help – Activating Emergency Services
The third component of DRSABCD involves calling emergency services immediately. This step is crucial because professional medical help will ultimately be required for most serious emergencies.
When calling emergency services, provide clear, concise information including the exact location, nature of the emergency, and current condition of the victim. Stay calm and answer all questions from the dispatcher, as they may provide life-saving instructions over the phone.
If multiple people are present, assign someone specific to make the call while you continue with the DRSABCD protocol. This ensures that help is on the way while you provide immediate care.
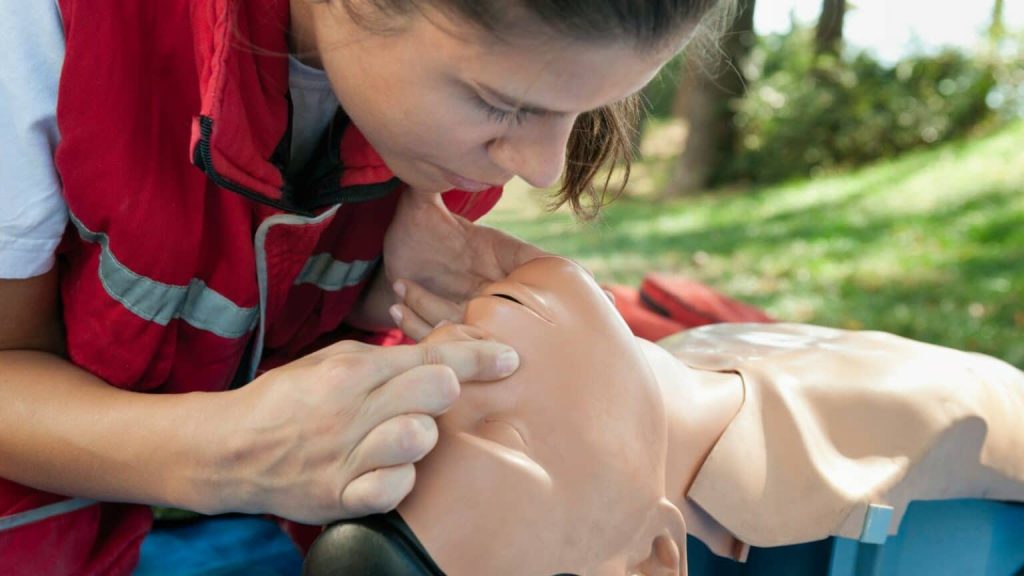
Step 4: Airway Management in DRSABCD
Proper airway management represents a critical component of the DRSABCD sequence. An obstructed airway can quickly become life-threatening, making this step essential for unconscious victims.
The head-tilt, chin-lift technique is the standard method for opening airways in unconscious patients. Place one hand on the forehead and gently tilt the head back while lifting the chin with your other hand. This simple maneuver often clears minor obstructions.
However, if you suspect spinal injuries, use the jaw-thrust technique instead. Additionally, check for visible obstructions in the mouth and remove them carefully if safe to do so.
Step 5: Breathing Assessment in DRSABCD
The fifth step of DRSABCD involves checking whether the victim is breathing normally. This assessment must be done quickly but thoroughly, as breathing problems require immediate intervention.
Look for chest movement, listen for breathing sounds, and feel for air movement on your cheek. Normal breathing should be regular and effortless. Gasping, very slow breathing, or no breathing at all indicates a serious emergency.
If the person is breathing normally, place them in the recovery position to maintain their airway. However, if breathing is absent or abnormal, immediately proceed to the next DRSABCD step.
Step 6: CPR – The Heart of DRSABCD
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) forms the cornerstone of the DRSABCD protocol when breathing and circulation are compromised. Proper CPR technique can maintain blood flow to vital organs until professional help arrives.
Begin chest compressions by placing the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, between the nipples. Place your other hand on top, interlacing your fingers. Push hard and fast at least 2 inches deep at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
After 30 compressions, provide 2 rescue breaths. Tilt the head back, lift the chin, seal your mouth over the victim’s mouth, and give 2 breaths that make the chest rise. Continue this cycle of 30 compressions and 2 breaths until help arrives.
Step 7: Defibrillation – Completing the DRSABCD Sequence
The final step in DRSABCD involves using an automated external defibrillator (AED) if available. These devices can restore normal heart rhythm in cases of cardiac arrest caused by certain abnormal heart rhythms.
Modern AEDs are designed for use by untrained bystanders and provide clear voice instructions. Simply turn on the device, attach the pads as illustrated, and follow the prompts. The AED will analyze the heart rhythm and advise whether a shock is needed.
If an AED is not immediately available, continue CPR until emergency services arrive. Remember, the combination of CPR and defibrillation significantly improves survival rates in cardiac arrest situations.
Training and Certification in DRSABCD
While understanding the DRSABCD protocol is valuable, proper training makes the difference between knowledge and life-saving action. Hands-on practice builds confidence and muscle memory that proves invaluable during real emergencies.
Professional training programs teach not only the technical aspects of DRSABCD but also how to remain calm under pressure. Furthermore, regular practice helps maintain skills and keeps responders current with the latest techniques and guidelines.
Many organizations offer comprehensive training that covers the entire DRSABCD sequence along with additional emergency response skills. These programs typically include practical scenarios that simulate real-world emergencies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in DRSABCD
Even well-intentioned responders can make errors that compromise the effectiveness of the DRSABCD protocol. Understanding these common mistakes helps ensure proper implementation during emergencies.
One frequent error involves rushing through the danger assessment step. Taking time to properly evaluate the scene prevents responders from becoming additional victims. Additionally, inadequate chest compression depth or rate reduces the effectiveness of CPR.
Another common mistake is hesitating to begin CPR due to fear of causing harm. However, the benefits of properly performed CPR far outweigh the risks when someone is in cardiac arrest.
The Importance of Regular DRSABCD Training
Skills deteriorate over time without practice, making regular training essential for maintaining DRSABCD competency. Studies show that CPR skills can decline significantly within just a few months without refresher training.
Regular practice also helps responders stay current with evolving guidelines and techniques. Medical organizations periodically update their recommendations based on new research and evidence.
Furthermore, repeated training builds confidence that enables responders to act quickly and effectively during real emergencies. This confidence can make the difference between hesitation and immediate action.
Take Action: Get Certified Today
The DRSABCD protocol represents a powerful tool for saving lives, but proper training is essential for effective implementation. Don’t wait until an emergency occurs to learn these critical skills.
CPR Memphis is an American Heart Association training site that offers comprehensive certification programs, including BLS certification in Memphis, PALS, and CPR and First Aid courses. All classes are stress-free and hands-on, providing the practical experience needed to confidently apply the DRSABCD protocol.
Whether you’re seeking initial CPR certification in Memphis or need to renew existing credentials, CPR Memphis offers the best CPR training in Memphis. Their expert instructors ensure that every participant masters the DRSABCD sequence and develops the confidence to respond effectively in emergencies.
Contact CPR Memphis today to schedule your training and join the ranks of prepared responders who can make a difference when it matters most. Remember, the life you save using the DRSABCD protocol could be someone you love.




