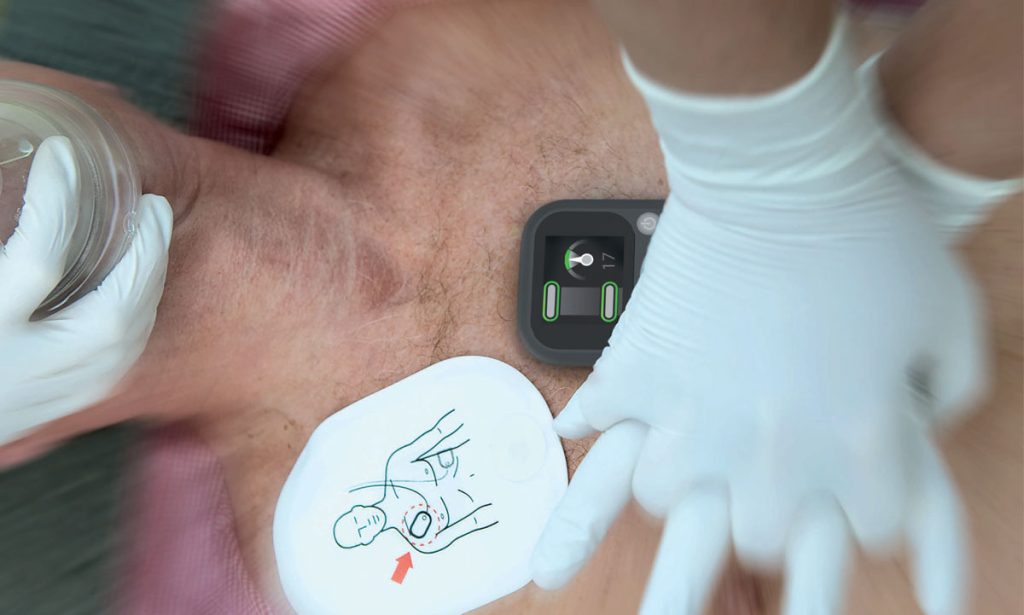
In the critical moments following cardiac arrest, every second counts. High-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) significantly increases survival rates, but maintaining optimal compression depth, rate, and recoil can be challenging even for experienced healthcare providers. This has led to the development of CPR feedback devices—tools designed to monitor and guide rescuers in real-time. But the question remains: do these feedback devices actually work in real cardiac arrest situations?
How Feedback Devices Monitor CPR Performance
CPR feedback devices employ various technologies to track critical parameters during resuscitation efforts. These sophisticated tools can simultaneously monitor multiple aspects of CPR quality, providing rescuers with instant guidance when it matters most.
Most devices track compression depth, ensuring rescuers reach the recommended 2-2.4 inches (5-6 cm) with each compression. They also monitor compression rate, helping maintain the ideal pace of 100-120 compressions per minute. Additionally, these devices evaluate chest recoil—a crucial but often overlooked component that allows the heart to refill between compressions.
Some advanced feedback devices can even detect compression fraction (the percentage of time compressions are being performed during a resuscitation) and hand positioning on the chest. Through visual displays, audio prompts, or haptic feedback, these devices communicate in real-time when adjustments are needed.
What is the Real-Time Feedback Device for CPR?
Several types of real-time feedback devices have emerged in recent years, each with unique approaches to monitoring and guiding CPR performance.
Accelerometer-Based Devices
These portable devices use accelerometer technology to measure chest compression parameters. Typically placed between the rescuer’s hands and the patient’s chest, they track the motion during compressions to calculate depth, rate, and recoil. Popular examples include the CPR STAT Pad, PocketCPR, and CPRmeter.
Force-Sensing Devices
Instead of measuring motion, these devices measure the force applied during compressions. This approach offers additional insights into the quality of compressions, particularly in patients with different chest compliance characteristics. The CPR Force Sensor is a common example in this category.
Integrated Monitor/Defibrillator Systems
Many modern defibrillators now incorporate CPR feedback functionality. Systems like the ZOLL R Series, Philips HeartStart MRx, and Physio-Control LIFEPAK include sensors that connect to the patient and provide feedback through the defibrillator’s display. These integrated systems offer comprehensive monitoring during resuscitation.
Visual Feedback Systems
Some innovative systems use camera technology and visual processing algorithms to analyze CPR performance without physical contact with the patient. The CPR PRO device uses this approach, providing feedback through a display visible to the rescuer.
What is True About CPR Feedback Devices?
When evaluating the impact of feedback devices on resuscitation outcomes, several important truths emerge from the research literature.
They Improve Consistency
One undeniable benefit of feedback devices is their ability to promote consistency in CPR delivery. Studies show that compression quality tends to deteriorate rapidly due to rescuer fatigue and distraction, even among trained professionals. Feedback devices help maintain consistent performance throughout the resuscitation effort.
A 2019 study published in the Journal of Emergency Medicine demonstrated that providers using feedback devices maintained proper compression depth for 83% of resuscitation time, compared to only 54% without feedback assistance.
They Enhance Training Effectiveness
Feedback devices have proven particularly valuable in CPR training scenarios. By providing immediate feedback during practice, these tools help learners develop proper technique and muscle memory. This translates to better performance during actual emergencies.
They Have Limitations
Despite their benefits, feedback devices aren’t perfect. Most current technologies cannot account for all patient variables, such as body size, chest wall compliance, or positioning surfaces. Furthermore, the devices themselves can occasionally malfunction or provide inaccurate readings if not properly positioned.
Do Feedback Devices Work in Real Cardiac Arrests? The Evidence
While the theoretical benefits of feedback devices are clear, their actual impact on survival outcomes in real cardiac arrest situations has been a subject of ongoing research. Let’s examine what the evidence tells us.
Hospital Setting Evidence
Several hospital-based studies have demonstrated improvements in CPR quality metrics when feedback devices are employed. A 2021 multicenter trial involving 1,586 in-hospital cardiac arrests found that resuscitation teams using feedback devices achieved proper compression depth 76% of the time, compared to 38% in the control group.
However, this improvement in CPR metrics hasn’t consistently translated to better survival rates. A systematic review published in the Resuscitation journal analyzed 11 studies and found that while feedback devices improved CPR quality parameters, they did not significantly improve survival to hospital discharge.
Pre-Hospital Setting Evidence
The evidence for feedback device effectiveness in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests shows similar patterns. A large-scale study by the Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium evaluated 15,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and found that while CPR metrics improved with feedback devices, there was no significant difference in survival rates.
Real-World Implementation Challenges
The research reveals several challenges that may limit the effectiveness of feedback devices in real-world scenarios:
- Interface distraction: Some rescuers report becoming fixated on the feedback display, potentially diverting attention from other important aspects of resuscitation.
- Implementation barriers: Incorporating new technologies into established resuscitation protocols requires training, maintenance, and sometimes workflow adjustments.
- Context sensitivity: Most studies evaluate feedback devices in controlled settings, which may not reflect the chaotic conditions of actual emergency scenarios.
Do Automated Real-Time Feedback Devices Improve CPR Quality?
Despite the mixed evidence on survival outcomes, research consistently shows that feedback devices do improve specific aspects of CPR quality when properly implemented.
Compression Depth Improvements
Multiple studies demonstrate that rescuers using feedback devices achieve and maintain proper compression depth more consistently. A 2022 meta-analysis of 17 studies found that feedback device use increased the percentage of compressions reaching target depth by an average of 35%.
Rate Compliance
Maintaining the ideal compression rate of 100-120 per minute can be challenging, especially during prolonged resuscitation efforts. Feedback devices have shown remarkable success in helping rescuers maintain appropriate rates, with one study showing a 68% improvement in rate compliance when feedback was provided.
Enhanced Chest Recoil
Complete chest recoil between compressions is essential for cardiac refilling but often neglected in practice. Feedback devices that monitor this parameter have been shown to increase complete recoil by approximately 25%, potentially improving cardiac output during CPR.
Team Performance Factors
Beyond individual rescuer performance, feedback devices can impact team dynamics during resuscitation. Research suggests that teams using feedback devices demonstrate better communication and coordination, with clearer role delineation and more efficient task switching during CPR.
Implementing Feedback Devices: Best Practices
For healthcare organizations considering the adoption of CPR feedback devices, several best practices can maximize their effectiveness:
Integration with Training
Feedback devices should be introduced during initial CPR training and integrated into regular practice sessions. This familiarity ensures that rescuers can use the devices effectively during actual emergencies without added stress or confusion.
Protocol Development
Clear protocols should specify when and how feedback devices are deployed during resuscitation efforts. These protocols should address practical considerations such as device placement, monitoring responsibilities, and response to feedback alerts.
Quality Improvement Programs
The data captured by many feedback devices can be invaluable for quality improvement initiatives. Regular review of this information allows organizations to identify systemic issues, target specific training needs, and track improvements over time.
Maintaining Human Judgment
While embracing technological assistance, organizations should emphasize that feedback devices supplement rather than replace clinical judgment. Rescuers should understand the limitations of these tools and recognize situations where human assessment may override automated feedback.
The Future of CPR Feedback Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the next generation of feedback devices promises even greater capabilities:
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Emerging systems are incorporating AI algorithms that can analyze multiple parameters simultaneously and provide more nuanced feedback based on patient-specific factors.
Augmented Reality Guidance
Some developers are exploring augmented reality interfaces that could overlay guidance directly onto the patient, eliminating the need for rescuers to shift focus to separate displays.
Comprehensive Resuscitation Analytics
Advanced data capture and analysis may soon allow feedback systems to evaluate the entire resuscitation effort, including medication timing, ventilation quality, and team performance metrics.
Conclusion: Do Feedback Devices Work in Real Cardiac Arrests?
The evidence suggests that CPR feedback devices do improve technical aspects of resuscitation quality, particularly compression depth, rate, and recoil. However, their impact on survival outcomes remains less definitive, highlighting the complex nature of cardiac arrest recovery.
For healthcare organizations and emergency medical services, feedback devices represent valuable tools in the broader context of comprehensive resuscitation quality improvement. When properly integrated with training, protocols, and quality initiatives, these devices can contribute to more consistent, high-quality CPR—a critical link in the chain of survival.
As technology advances and implementation strategies improve, the gap between enhanced CPR metrics and survival outcomes may narrow. In the meantime, feedback devices remain an important innovation in the ongoing effort to optimize resuscitation care and save lives.
Take Action: Improve Your CPR Skills Today
Want to learn more about CPR best practices and feedback technology? CPR Cincinnati offers comprehensive American Heart Association training courses that incorporate the latest evidence-based techniques and technologies.
Whether you’re seeking BLS certification in Cincinnati for healthcare professionals or basic CPR training, our hands-on courses provide the skills and confidence needed to respond effectively in emergencies.
Contact CPR Cincinnati today to schedule your CPR certification course and join the community of trained responders making a difference when every second counts. Our stress-free, engaging classes are taught by experienced instructors using state-of-the-art equipment, making us the best CPR training provider in the Cincinnati area.