The Critical First Minutes
When someone suffers a cardiac arrest, every second counts. In these critical situations, basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) can be a lifesaving technique that anyone can perform. CPR involves chest compressions and rescue breaths, which help maintain some blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain and other vital organs until advanced medical help arrives. However, as essential as basic CPR is, it raises an important question: Is it enough on its own, or are there more comprehensive techniques that can further improve the chances of survival?
This is where Basic Life Support (BLS) comes into play. BLS encompasses a broader range of life-saving skills and procedures beyond just CPR. It is a set of emergency medical procedures designed to provide initial care to a victim of cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, or other life-threatening emergencies. BLS builds upon the foundation of basic CPR by incorporating additional techniques and equipment to enhance the effectiveness of the response.
Understanding Basic CPR
Before delving into BLS, it’s crucial to understand the fundamentals of basic CPR. CPR involves two key steps: chest compressions and rescue breaths. Chest compressions involve applying firm pressure on the center of the chest at a specific rate to mimic the pumping action of the heart. Rescue breaths, on the other hand, involve providing artificial respiration by blowing air into the victim’s mouth or nose.
Basic CPR is an essential skill that everyone should learn, as it can be the difference between life and death in an emergency. When performed correctly and promptly, it can help maintain blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain and other vital organs until advanced medical assistance arrives. However, basic CPR has its limitations, particularly in terms of its duration and overall effectiveness in complex medical emergencies.
What is Basic Life Support (BLS)?
Basic Life Support (BLS) is a comprehensive set of emergency medical procedures that go beyond basic CPR. It includes various techniques and interventions aimed at providing immediate care to individuals experiencing life-threatening emergencies, such as cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, choking, or other critical medical conditions.
The components of BLS include:
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): BLS includes the administration of high-quality CPR, which involves chest compressions and rescue breaths, as in basic CPR.
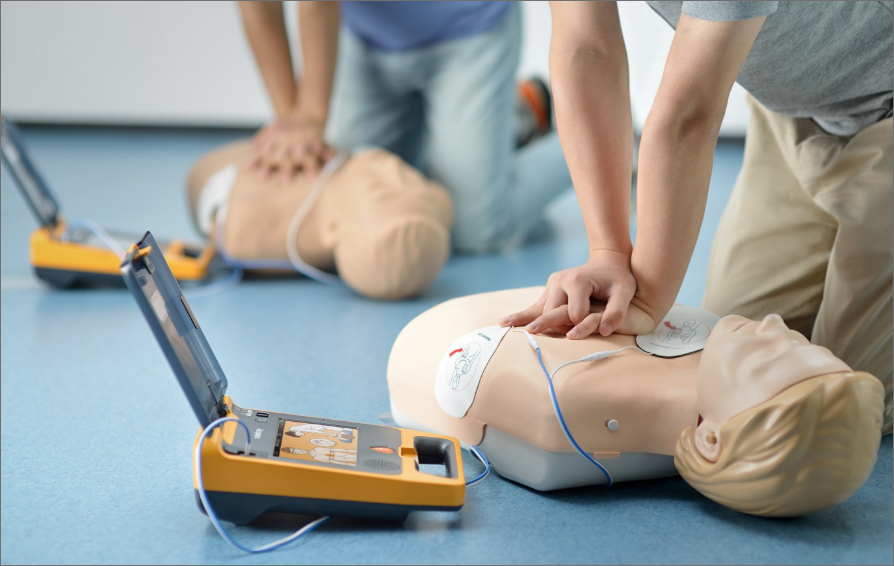
- Automated External Defibrillator (AED) use: BLS training teaches the proper use of AEDs, which are portable devices that can deliver an electric shock to restart the heart’s rhythm in cases of sudden cardiac arrest.
- Rescue breathing and airway management: BLS providers learn advanced techniques for opening and maintaining a victim’s airway, as well as methods for providing rescue breaths more effectively.
- Recognizing and responding to various medical emergencies: BLS training covers how to identify and respond to different types of medical emergencies, such as choking, drowning, seizures, and other critical situations.
BLS builds upon the foundation of basic CPR by incorporating additional life-saving techniques and equipment. It is designed to provide more comprehensive care until advanced medical support arrives or until the victim can be transported to a healthcare facility.
BLS training and certification are essential for healthcare professionals, emergency responders, and individuals who may encounter medical emergencies in their personal or professional lives. Proper BLS training ensures that individuals are equipped with the knowledge and skills to respond effectively in critical situations, potentially increasing the chances of survival and better patient outcomes.
Advantages of BLS over Basic CPR
While basic CPR is a crucial lifesaving skill, Basic Life Support (BLS) offers several advantages that can significantly improve patient outcomes and increase the chances of survival in medical emergencies.
- Improved Chances of Survival and Better Patient Outcomes: BLS training equips individuals with a broader range of techniques and interventions, allowing them to provide more comprehensive care. This increased level of preparedness can lead to better patient outcomes and a higher likelihood of survival, especially in complex medical emergencies.
- Ability to Handle More Complex Medical Emergencies: BLS training goes beyond cardiac arrest situations and covers a wide range of medical emergencies, including choking, drowning, seizures, and other critical conditions. BLS providers learn how to recognize and respond appropriately to these diverse scenarios, increasing their ability to provide effective care in various situations.
- Use of Advanced Airway Management Techniques and Equipment: BLS training includes advanced airway management techniques, such as the use of bag-valve masks, oral and nasal airways, and suction devices. These techniques and equipment can help ensure proper oxygenation and ventilation, which are crucial for patient survival and recovery.
- Integration of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs): One of the key components of BLS is the use of AEDs. These portable devices can deliver an electric shock to restart the heart’s rhythm in cases of sudden cardiac arrest. BLS providers learn how to properly operate AEDs, increasing the chances of successful defibrillation and improving patient outcomes.
While basic CPR remains a vital skill, BLS offers a comprehensive approach to emergency medical care. By incorporating advanced techniques, equipment, and a broader understanding of medical emergencies, BLS providers are better equipped to respond effectively and potentially save more lives.
Scenarios Where BLS is Crucial
While basic CPR can be a lifesaving technique in cardiac arrest situations, there are scenarios where it may not be sufficient, and the advanced skills learned in Basic Life Support (BLS) become crucial.
- Prolonged Cardiac Arrest: In cases of prolonged cardiac arrest, where the victim has been without a pulse for an extended period, basic CPR alone may not be enough. BLS training equips individuals with advanced airway management techniques, such as the use of bag-valve masks and oral/nasal airways, ensuring better oxygenation and ventilation until advanced medical support arrives.
- Respiratory Distress: Individuals suffering from respiratory distress, such as those experiencing asthma attacks, severe allergic reactions, or other breathing difficulties, may require interventions beyond basic CPR. BLS providers learn how to recognize and respond to these situations, including proper positioning, airway management, and the use of supplemental oxygen if available.
- Choking Emergencies: Choking can quickly become a life-threatening situation if not addressed promptly. BLS training teaches specific techniques for dislodging obstructions from the airway, such as abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver) and back blows, which can be crucial in preventing further complications or even death.
- Drowning Incidents: In cases of drowning, time is of the essence, and basic CPR alone may not be sufficient. BLS providers learn specialized techniques for managing drowning victims, including proper victim positioning, airway management, and rescue breathing, increasing the chances of successful resuscitation.
- Emergency Situations in Remote or Isolated Areas: In remote or isolated areas where advanced medical support may take longer to arrive, having trained BLS providers on-site can be invaluable. Their ability to provide comprehensive care, including airway management, oxygen administration (if available), and other interventions, can significantly increase the chances of survival until further assistance arrives.
While basic CPR is an essential skill, having trained BLS providers readily available can make a significant difference in various medical emergencies, particularly those requiring more advanced interventions and specialized care.
Training and Certification for BLS
Obtaining Basic Life Support (BLS) certification requires proper training and preparation. BLS courses are typically offered by authorized training centers or organizations, such as the American Heart Association, American Red Cross, or other recognized providers.
The process of obtaining BLS certification typically involves the following steps:
- Course Enrollment: Individuals interested in becoming BLS certified must enroll in a BLS course offered by an authorized training provider. These courses are designed to provide comprehensive theoretical and practical training in lifesaving techniques.
- Classroom Instruction: BLS courses involve classroom instruction led by certified instructors. During these sessions, participants learn about various aspects of BLS, including CPR techniques, AED use, airway management, and how to respond to different medical emergencies.
- Hands-on Practice: A significant portion of BLS training is dedicated to hands-on practice. Participants will have the opportunity to practice skills such as chest compressions, rescue breaths, and other techniques on specialized manikins, allowing them to develop the necessary muscle memory and confidence.
- Skills Assessment: To become certified, participants must demonstrate proficiency in the required BLS skills. This typically involves a practical skills assessment, where instructors evaluate each participant’s ability to perform various lifesaving techniques effectively.
- Written Exam: In addition to the practical assessment, most BLS courses also include a written exam to evaluate the participant’s knowledge of BLS principles, protocols, and decision-making processes.
- Certification: Upon successful completion of the course, practical skills assessment, and written exam, participants will receive their BLS certification, which is typically valid for two years.
Regular recertification is essential to ensure that BLS providers maintain their knowledge and skills. Most organizations require recertification every two years, which may involve attending a refresher course or completing a skills assessment to renew the certification.
It is crucial to emphasize that BLS certification is not just for healthcare professionals or emergency responders. Individuals from various backgrounds, including teachers, coaches, lifeguards, and even concerned citizens, can benefit from obtaining BLS certification. Having these lifesaving skills can make a significant difference in emergency situations, potentially saving lives until advanced medical support arrives.
Conclusion
If you live in the Cincinnati area and want to gain lifesaving skills, consider getting CPR and BLS certified with CPR Cincinnati. As an American Heart Association training site, they offer top-notch, hands-on training for initial certifications and renewals in BLS for Healthcare Providers, ACLS, PALS, and CPR and First Aid courses. Their stress-free classes ensure you receive the best CPR certification Cincinnati has to offer.
Don’t wait until it’s too late – equip yourself with the knowledge and confidence to respond effectively in emergencies. With BLS certification Cincinnati from CPR Cincinnati, you’ll learn advanced techniques like airway management, AED use, and how to handle complex situations beyond basic CPR.
Gaining these crucial skills doesn’t just benefit healthcare workers – BLS certification Cincinnati is valuable for anyone who wants to be prepared, from teachers and coaches to concerned citizens. You never know when you may need to step in and save a life.