The Essential Role of AEDs in Enhancing CPR Outcomes
Imagine a bustling shopping mall on a Saturday afternoon. Suddenly, a man collapses, clutching his chest. Within moments, he’s unresponsive and not breathing. This scenario, all too common across the United States, is a stark reminder of the sudden and devastating nature of cardiac arrest.
Sudden cardiac arrest is a leading cause of death in America, striking without warning and affecting people of all ages and fitness levels. When every second counts, the difference between life and death often hinges on immediate and effective intervention. This is where the critical interplay between Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) comes into focus.
Understanding CPR
CPR is a life-saving technique that’s been around for decades. It involves chest compressions and, in some cases, rescue breaths to manually pump blood through the body and provide oxygen to vital organs. When performed correctly, CPR can be the difference between a victim surviving long enough for advanced medical help to arrive or succumbing to cardiac arrest within minutes.
The process works by mimicking the heart’s pumping action, circulating oxygen-rich blood to the brain and other critical organs. This buys precious time, potentially preventing irreversible organ damage or death. However, while CPR is undoubtedly crucial, it has limitations. CPR alone cannot restart a heart that has stopped or correct an abnormal heart rhythm. This is where defibrillation comes into play.
The Role of Defibrillation
Defibrillation is the process of delivering a controlled electric shock to the heart to restore its normal rhythm. When a person experiences sudden cardiac arrest, their heart often enters a chaotic pattern called ventricular fibrillation. In this state, the heart quivers ineffectively instead of pumping blood. A defibrillator can send an electric current through the heart, momentarily stopping all electrical activity. This gives the heart a chance to “reset” and potentially resume a normal, effective rhythm.
Traditionally, defibrillation was only available in hospitals or when performed by highly trained emergency medical professionals. However, the advent of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) has revolutionized emergency cardiac care, bringing this life-saving technology into public spaces and the hands of bystanders.
Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs)
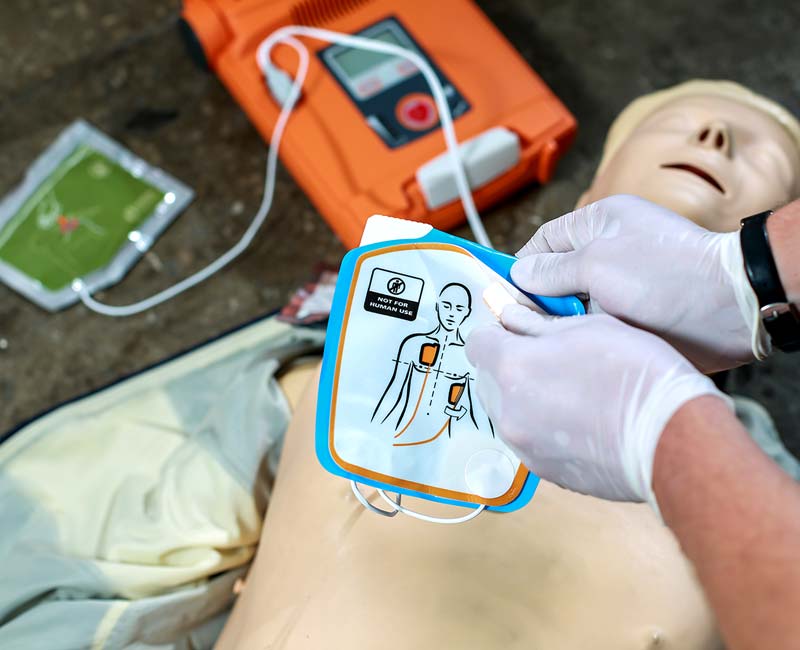
Automated External Defibrillators, or AEDs, are portable electronic devices designed to analyze heart rhythms and deliver a shock to victims of sudden cardiac arrest when necessary. These user-friendly devices have become a critical link in the chain of survival, effectively bridging the gap between CPR and professional medical intervention.
AEDs work by guiding users through the resuscitation process with voice and visual prompts. Once activated, the device analyzes the victim’s heart rhythm through adhesive electrodes placed on the chest. If a shockable rhythm is detected, the AED charges itself and prompts the user to deliver the shock by pressing a button. This process can be repeated as necessary until emergency medical services arrive.
The true power of AEDs lies in their ability to bring defibrillation to the scene of a cardiac emergency within the critical first few minutes. When combined with effective CPR, AEDs significantly increase the chances of survival. Studies have shown that for every minute that passes without CPR and defibrillation, the likelihood of survival decreases by 7-10%. However, when bystander CPR is provided and an AED is used before EMS arrival, survival rates can double or even triple.
Using AEDs Effectively
While AEDs are designed to be user-friendly, proper training is crucial for their effective use. The basic steps for operating an AED include:
- Turning on the device
- Following the voice and visual prompts
- Attaching the electrode pads to the victim’s bare chest
- Allowing the AED to analyze the heart rhythm
- Delivering a shock if instructed by the device
- Resuming CPR immediately after the shock is delivered or if no shock is advised
It’s important to note that AEDs should be used in conjunction with CPR, not as a replacement. High-quality CPR should be performed before the AED arrives and between analyses and shocks. This continuous chest compression helps maintain blood flow to vital organs while the AED works to restore a normal heart rhythm.
AED Accessibility and Public Awareness
The effectiveness of AEDs in public settings has led to their increased placement in locations such as airports, shopping centers, sports facilities, and office buildings. Many states have even mandated AED placement in certain public spaces. However, the mere presence of AEDs isn’t enough – public awareness and education are crucial.
Efforts to increase public awareness about AEDs include:
- Clear signage indicating AED locations
- Community education programs
- Integration of AED training into CPR courses
- Promotion of AED use through various media channels
Legal considerations, including Good Samaritan laws that protect lay rescuers who act in good faith to help others, have also been implemented in many jurisdictions to encourage bystander intervention.
Conclusion
The introduction of AEDs has dramatically improved the chances of survival for victims of sudden cardiac arrest. By bridging the crucial gap between immediate bystander CPR and the arrival of professional medical help, AEDs have become a vital link in the chain of survival.
However, the full potential of these life-saving devices can only be realized through proper training and increased public awareness. Understanding how to perform CPR and use an AED effectively can make the difference between life and death in an emergency.
We strongly encourage all readers to take action and enroll in CPR certification courses. For those in the Louisville area, CPR Louisville offers an unparalleled opportunity to gain these critical skills. As an American Heart Association training site, CPR Louisville provides the gold standard in CPR and AED training. They offer a wide range of courses including BLS for Healthcare Providers, ACLS, PALS, and CPR and First Aid, all designed to meet various needs and skill levels.
What sets CPR Louisville apart is its commitment to stress-free, hands-on learning. All classes provide practical experience in a supportive environment, ensuring you’ll leave feeling confident in your ability to respond in an emergency. Whether you’re seeking initial certification or need to renew your credentials, CPR Louisville has flexible options to fit your schedule.
Remember, in a cardiac emergency, every second counts. By enrolling in a CPR certification course at CPR Louisville, you’re not just gaining a valuable skill – you’re preparing yourself to potentially save a life. Don’t wait for an emergency to wish you knew what to do. Take the step today to become certified in CPR and AED use.
Enroll now at CPR Louisville and experience the best CPR training in Louisville. Your decision to get certified could one day make the difference between life and death for someone in need.