Introduction
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a critical life-saving skill that can mean the difference between life and death in emergencies. As medical knowledge advances and new research emerges, CPR guidelines are periodically updated to ensure the most effective techniques are used. For healthcare professionals and trained responders, staying current with these changes is not just important—it’s essential.
In recent years, several key modifications have been made to CPR guidelines. These changes reflect the latest understanding of cardiac arrest management and aim to improve survival rates. Whether you’re due for recertification or simply want to stay informed, this article will highlight the most significant updates you need to know.
Key Updates in CPR Techniques
Chest Compressions: One of the most notable changes in recent guidelines is emphasizing high-quality chest compressions. The recommended rate has been slightly modified to 100-120 compressions per minute, replacing the previous “at least 100” recommendation. This specific range ensures that compressions are neither too slow to maintain adequate blood flow nor too fast to allow proper chest recoil.
Depth adjustments have also been made. Current guidelines specify a compression depth of 2-2.4 inches (5-6 cm) for adults. This is a slight change from previous guidelines and aims to strike a balance between providing enough force to circulate blood effectively without risking injury to the chest cavity.
Rescue Breaths: While compression-only CPR has gained traction for bystanders, rescue breaths remain crucial for trained professionals. The breath-to-compression ratio remains at 30:2 for adults, but there’s an increased emphasis on minimizing interruptions to chest compressions. Guidelines now stress that each breath should take only one second, with just enough volume to see the chest rise.
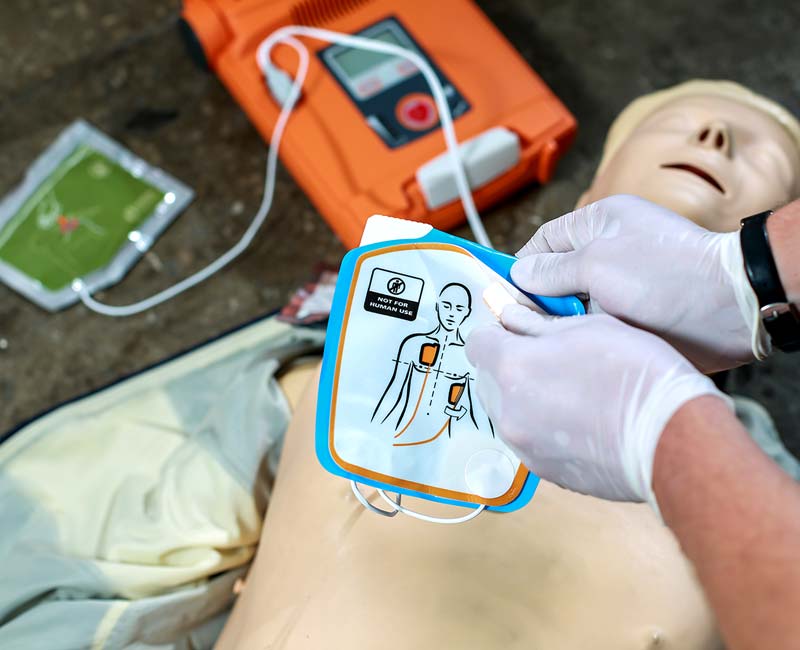
Use of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs)
The integration of AEDs into CPR protocols has been further refined in recent guideline updates. AEDs remain a crucial tool in improving survival rates for sudden cardiac arrest, and the latest recommendations emphasize their prompt and effective use.
Updated protocols for AED use now stress the importance of minimizing pauses in chest compressions during AED operation. Rescuers are advised to continue compressions while the AED is being prepared and to resume compressions immediately after each shock is delivered. This ensures that vital blood circulation is maintained throughout the resuscitation process.
The guidelines also highlight the importance of clear communication between rescuers during AED use. One rescuer should be designated to operate the AED while others continue compressions, switching roles if necessary to prevent fatigue.
Integration with CPR has been further streamlined. Current recommendations suggest that as soon as an AED arrives, it should be turned on and attached to the patient without delay. However, CPR should not be interrupted during this process. The emphasis is on a seamless transition between manual CPR and defibrillation, maximizing the chance of successful resuscitation.
Special Considerations
Pediatric CPR Modifications: Recent guideline changes have also addressed pediatric CPR. For children, the compression depth recommendation has been updated to at least one-third of the anterior-posterior diameter of the chest. This typically translates to about 2 inches (5 cm) in most children and infants, but not more than 2.4 inches (6 cm) in children.
The compression-to-ventilation ratio for two-rescuer CPR in children has been maintained at 15:2, differing from the adult 30:2 ratio. This reflects the higher importance of ventilation in pediatric resuscitation due to the likelihood of respiratory causes in pediatric cardiac arrest.
Changes in Drowning Victim Resuscitation: Guidelines for resuscitating drowning victims have also seen updates. The latest recommendations emphasize starting with five initial rescue breaths before beginning chest compressions, due to the likelihood of hypoxia being the primary cause of cardiac arrest in drowning cases.
Training and Certification Process Updates
As CPR guidelines evolve, so do the training and certification processes. These updates ensure that both new learners and those renewing their certifications are equipped with the most current knowledge and skills.
New Elements in CPR Courses: Recent CPR courses have incorporated several new elements to reflect the latest guidelines. These include:
- Enhanced focus on high-quality CPR: Courses now place greater emphasis on proper compression technique, including rate, depth, and allowing full chest recoil.
- Team dynamics: There’s increased attention to effective communication and coordination in multi-rescuer scenarios.
- Use of feedback devices: Many courses now incorporate real-time feedback devices to help learners perfect their compression technique.
- Scenario-based learning: More realistic scenarios are being used to better prepare rescuers for real-life situations.
Changes in Certification Renewal Requirements: Certification renewal processes have also been updated to ensure that skills remain sharp and knowledge current. Key changes include:
- More frequent skill checks: Many organizations now require more frequent hands-on skill evaluations between full recertification periods.
- Blended learning options: A combination of online learning and in-person skill verification is becoming more common, offering greater flexibility for recertification.
- Emphasis on continuous learning: There’s a growing focus on ongoing education between formal recertifications, often through online resources or mobile apps.
- Shorter recertification cycles: Some organizations have shortened the time between required recertifications to ensure skills and knowledge remain up-to-date.
Emphasis on Early Recognition and Response
Updated Signs of Cardiac Arrest: Recent guidelines have refined the signs that rescuers should look for when assessing a potential cardiac arrest. The key indicators now emphasized are:
- Absence of responsiveness
- Absence of normal breathing or only gasping
- No detectable pulse (for healthcare providers)
The guidelines stress that these assessments should be done quickly, ideally within 10 seconds, to avoid delaying the start of CPR.
Importance of Quick Action and Calling for Help: There’s an increased emphasis on the critical nature of early intervention. Guidelines now stress the importance of:
- Immediate activation of emergency response systems
- Starting chest compressions as quickly as possible
- Rapid retrieval and use of an AED if available
The concept of the “Chain of Survival” continues to be emphasized, highlighting how each step – from early recognition to post-resuscitation care – is crucial for improving outcomes.
Conclusion
Renewing your CPR certification is more than just a professional requirement—it’s a commitment to providing the best possible care for your patients. Regular renewal ensures you’re equipped with the latest knowledge and techniques, confident in your abilities, and ready to act decisively in emergencies.
Encouragement to prioritize timely renewal with CPR Memphis
Don’t let your CPR certification lapse. Mark your renewal date on your calendar and plan to complete the process well before your current certification expires. For medical professionals in the Memphis area, we highly recommend CPR Memphis for your certification renewal needs.
CPR Memphis is an American Heart Association training site that offers both initial certifications and renewals in a variety of crucial life-saving courses, including:
- BLS for Healthcare Providers
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS)
- CPR and First Aid courses
What sets CPR Memphis apart is its commitment to providing stress-free, hands-on learning experiences. Their expert instructors ensure that you not only meet the requirements for recertification but also gain practical skills and confidence in a supportive environment.
By choosing CPR Memphis for your renewal, you’re guaranteeing that you’ll receive top-quality training aligned with the latest American Heart Association guidelines. Their courses are designed to fit into your busy schedule while providing the comprehensive training you need to stay at the top of your field.
Remember, in a cardiac emergency, every second counts, and your up-to-date skills could make all the difference. Prioritize your CPR certification renewal in Memphis through CPR Memphis– widely recognized as the best CPR training provider in Memphis!
Take action today to maintain your life-saving skills. Visit CPR Memphis’s website or contact them directly to schedule your renewal course. Invest in your professional development, ensure compliance with job requirements, and most importantly, be prepared to provide the highest standard of care when it matters most.